Utilization of Corn Cob and TiO2 Photocatalyst Thin Films for Dyes Removal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2983Keywords:
Malachite Green, Acid Yellow 17, Immoblization, Plackett Burman, Response Surface MethodologyAbstract
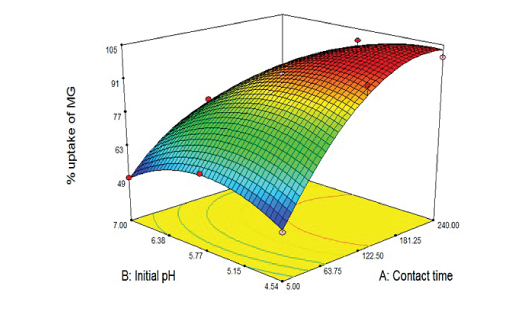
The effectiveness of using TiO2 and corn cob films to remove Malachite Green oxalate (MG) and Acid Yellow 17 (AY 17) from binary dye solution was studied. The immobilization method in this study can avoid the filtration step which is not suited for practical applications. Batch studies were performed under different experimental conditions and the parameters studied involved initial pH of dye solution, initial dye concentration and contact time and reusability. The equilibrium data of MG and AY 17 conform to Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm model, respectively. The percentage removal of MG remained high after four sorption cycles, however for AY 17, a greater reduction was observed. The removal of both dyes were optimized and modeled via Plackett- Burman design (PB) and Response Surface Methodology (RSM). IR spectrum and surface conditions analyses were carried out using fourier-transform infrared spectrophotometer (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM), respectively.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
