Synthesis, DFT, and Molecular Docking Studies of Anti-cancer Imidazolidine-2,4-dione and Thiazolidine-2,4-dione Derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2025.9326Abstract
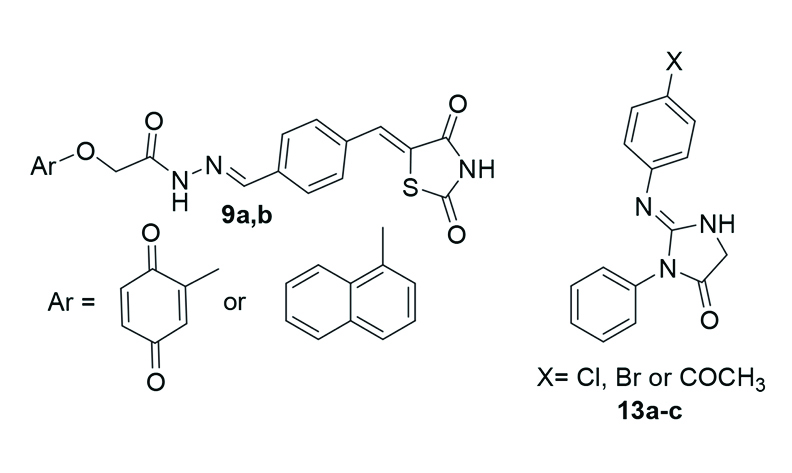
Novel families of thiazolidine-2,4-dione and imidazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives were synthesized. Thiazolidine-2,4-dione 3 was prepared using chloroacetic acid and thiourea, followed by condensation with terephthalaldehyde to form 4-((2,4-dioxothiazolidine-5-ylidene)methyl)benzaldehyde 4. This compound reacted with 2-aryloxyacetohydrazides 8a-b to yield Schiff bases 9a-b. Imidazolidine-2,4-diones 13a-c were synthesized via cyclizing of anilines 10a-c, urea 11, and chloroacetic acid 12. The compounds 9a-b and 13a-c were evaluated for antitumor activity against the Caco-2 cell line, compounds 13b and 13c exhibiting the highest potency (IC50 values of 41.30 ± 0.07 μM and 109.2 ± 0.027 μM, respectively). DFT calculations, including HOMO-LUMO analysis, energy gap estimation, and molecular docking, were conducted to evaluate and optimize the molecular properties of the target compounds.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Osama Alharbi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
