HPLC-DAD analysis, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of fruit extracts from Pistacia atlantica Desf.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2025.9317Abstract
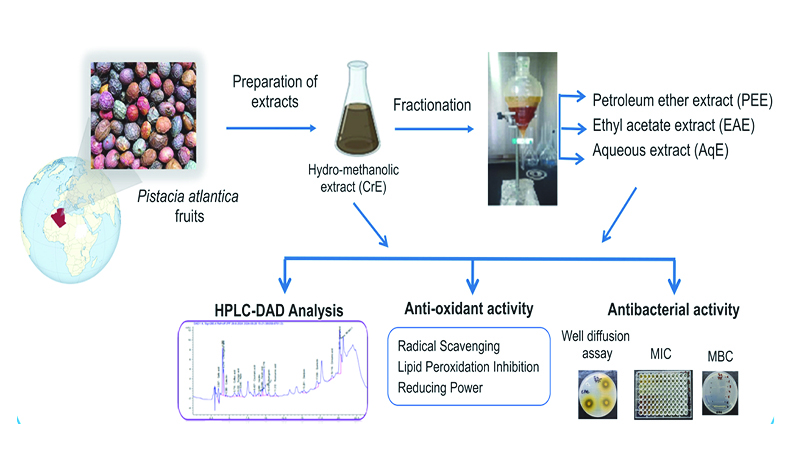
Pistacia atlantica is commonly used in traditional medicine to treat various diseases in Algeria. This study was carried out to investigate the antioxidant potential and antibacterial properties of fruit extracts. The results indicated various amounts of polyphenols and flavonoids in different extracts. Quercetin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid and methyl gallate were the dominant constituents in the ethyl acetate extract (EAE) and crude extract (CrE) quantified by HPLC-DAD. EAE was the most active in scavenging DPPH and hydroxyl (OH.) radicals, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), reducing power and total antioxidant capacity. All extracts have the ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation. A broad spectrum of antibacterial effects (10.66 to 29.33 mm) was obtained. In addition, the time-kill assay and the MBC/MIC ratio indicated that all extracts were bactericidal against most of the test bacteria and their combination with antibiotics showed remarkable synergistic effect. The findings of this study suggest that medicinal plant is a potential source of natural antioxidant and antibacterial compounds, which could be used where these kind of activities are warranted.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Younes Douffa, Karima Saffidine, Nour Elhouda Belabes, Nadjet Azzi, Haifaa Laroui, Hafsa Silini Cherif, Thoraya Guemmaz, Fatima Zerargui, Abderahmane Baghiani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
