Synthesis, characterization, DFT investigation and in silico anti-eczema evaluation of a novel thiazolidinone derivative
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.9111Abstract
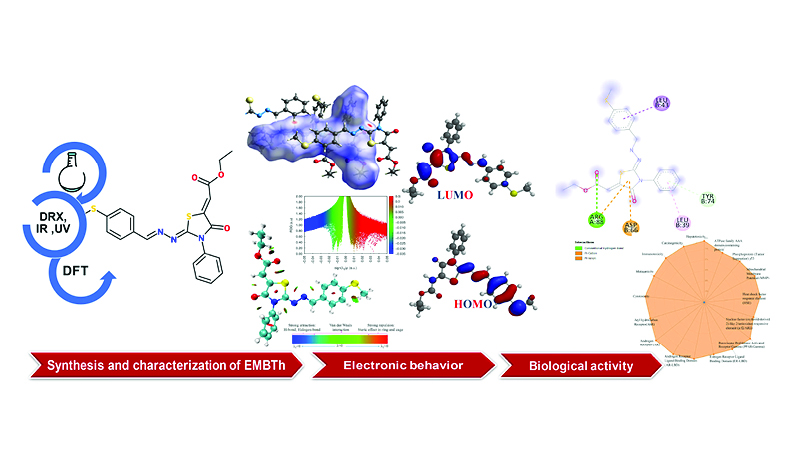
A new thiazolidinone derivative, (Z)-ethyl 2-((E)-2-((E)-(4-(methylthio) benzylidene) hydrazono)-4-oxo-3-phenylthiazolidin-5-ylidene) acetate (EMBTh), was synthesized via condensation method. This study employs a multidisciplinary approach, including compound characterization, molecular properties evaluation, and biological activity analysis. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SC-XRD) revealed that the compound crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with the P21/c space group. A theoretical model of EMBTh has been developed and substantiated by comparing SC-XRD results with theoretical calculations using density functional theory (DFT), employing the B3LYP function at a 6-311++G(d,p) level of theory. The study also explores the electronic behavior of the molecule and its molecular interactions, especially highlighting van der Waals forces via analysis of the molecular frontier orbitals and Hirshfeld surface. The results underscore the stability of the molecule and the significant contribution of hydrogen bonds to the crystal packing. Moreover, we conducted a molecular docking study to evaluate the anti-eczema activity of the EMBTh compound. The results revealed a good affinity in inhibiting the receptor (IL-4Rα), pinpointing the therapeutic potential of EMBT against the target protein of atopic eczema.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amine Ould Rabah, Abdelmadjid Benmohammed, Abdelkader Chouaih, Meriem Goudjil, Rachida Rahmani, Nour El Houda Belkafouf, Mohammed Hadj Mortada Belhachemi, Fatima Zohra Boudjenane, Ayada Djafri, Nourdine Boukabcha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
