A Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Quinoline Derivatives as Antibacterial Drug
Novel Quinoline Derivatives as Antibacterial Drug
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8484Abstract
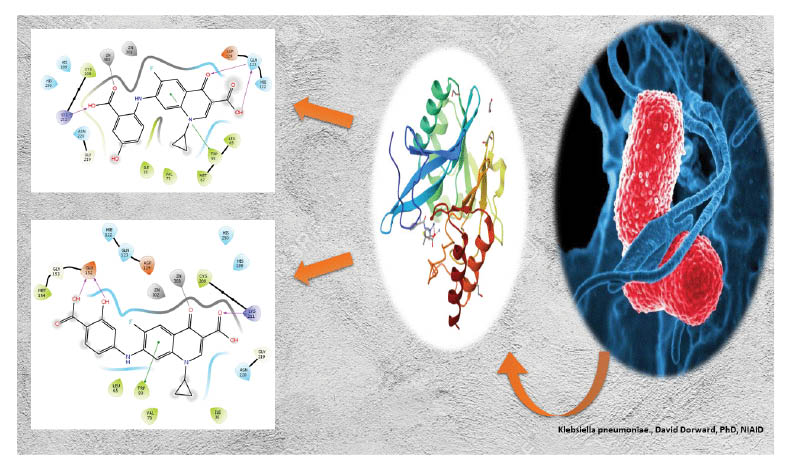
Quinoline and its derivatives are a family with unique medicinal properties, including antibacterial effects. It was assumed that the four Quinoline Derivatives Q1 , Q2, Q3 and Q4 had significant activity against pathogenic bacteria. These compounds were synthesized and characterization by TLC, IR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR analyses. The biological activity of compound Q1 was IZ (19 ± 0.22) against Klebsiella pneumoniae, IZ (18 ± 0.22) against Bacillus subtilis, IZ (17 ± 0.22) against Staphylococcus aureus. Q2 was IZ (18 ± 0.22) against both Klebsiella pneumoniae and Bacillus subtilis. Q3 was IZ (17 ± 0.22) against staphylococcus aureus. Q4 was IZ (21 ± 0.22), where showed a higher inhibitory activity against E. coli, than that of ciprofloxacin. These results demonstrate the potential of the synthesized compounds to work as antibacterial drugs against these strains by inhibiting or deactivating the target proteins.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Maryam Jamaal, Prof. Dr. Mohammed Oday Ezzat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
