Synthesis of bone meal-derived 4-carboxyphenylboronic acid functionalized sulfur and nitrogen co-doped graphene quantum dots nanoprobe for sialic acid sensing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8436Abstract
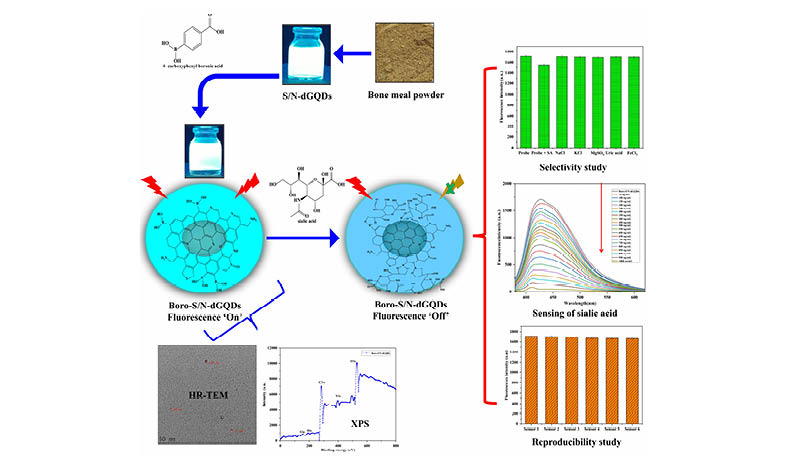
Detecting sialic acid using sensor-based technology in milk-based products is crucial. Therefore, present work reported the sulfur and nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots from bone meal functionalized with boronic acid (Boro-S/N-dGQDs) nanoprobe for sialic acid sensing applications. Briefly, S/N-dGQDs were functionalized with 4-carboxyphenylboronic acid to improve performance of fluorescent sensors for detection of sialic acid. The boronic acid surface decorating on S/N-dGQD was confirmed by several spectral characterizations. Addition of varying quantities of sialic acid results in a directly proportionate correlation to fluorescence quenching. As a result, it has a broad linear range of 50 ng/mL to 1000 ng/mL and a limit of detection of 6.04 ng/mL. It also displayed remarkable selectivity, likely due to interaction of sialic acid-containing 1,2-diol with hydroxyl group of Boro-S/N-dGQDs nanoprobe. Boro-S/N-dGQDs demonstrated good stability, reproducibility and real-time analysis of different milk-based products for presence of sialic acid confirmed practicability of fluorescent Boro-S/N-dGQDs sensor.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Sopan Nangare, Pratik Yeole, Zamir Khan, Ashwini Patil, Bhushankumar Sathe, Sanjaykumar Bari, Pravin Onkar Patil

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
