Exploring a substitute for hydrogen peroxide in Fenton process – A case study on the COD removal of Acid Orange 8
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8183Abstract
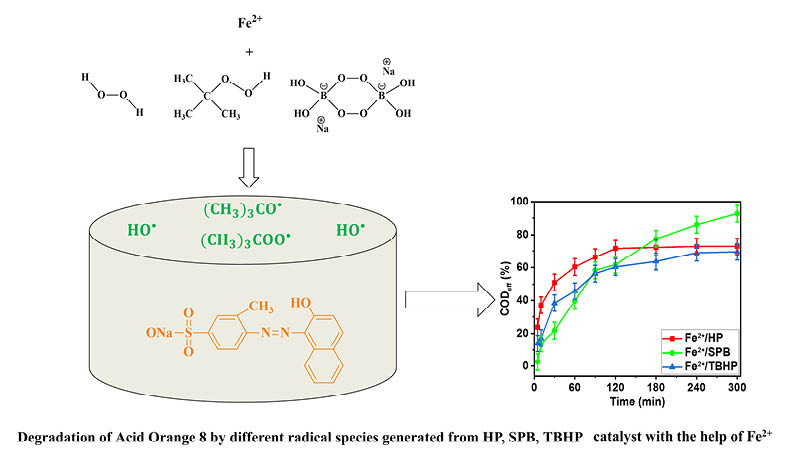
Hydrogen peroxide (HP) is widely used in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). This study evaluates the chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency of Acid Orange 8 (AO 8) at a higher concentration by modified Fenton processes using substituted HP such as tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) and sodium perborate (SPB) and sodium persulphate (SPS) as oxidants. Under optimal conditions, COD removal was found to be 72.8 and 58.9% at pH 3.0 and 6.5 in the Fenton process in 300 min. The COD removal efficiency of different systems is in the order: Fe2+/SPB>Fe2+/HP>Fe2+/TBHP>Fe2+/SPS indicating the possibility of using SPB as a substitute for HP and SPS. The order of efficiency is attributed, among other factors, to their ability to produce HO. radicals. Various anions are shown to exhibit an inhibitory effect in the order: I->Br->F->Cl->SO42->NO3-. The inhibitory effect of Cl- is observed at higher concentrations than F- and Br-, even though I- displays inhibition at all concentrations. Finally, COD removal kinetics and the degradation mechanism, based on the identified intermediate products, were determined in this study.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 TSUNGOM MULAI, JOHN ELISA KUMAR, WANSHANLANG KHARMAWPHLANG, Mihir Kumar Sahoo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
