In Situ Preparation, Structure, Photoluminescence and Theoretical Study of an Unusual Bismuth Complex
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2897Keywords:
bismuth, photoluminescence, in situ, TDDFT, X-ray diffractionAbstract
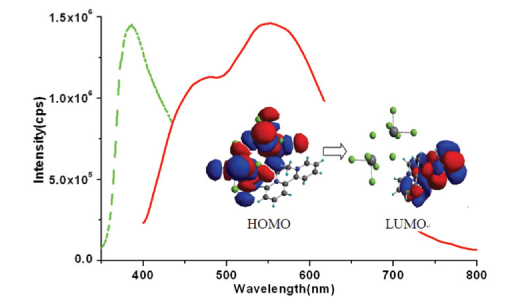
A novel bismuth photoluminescent material, (N,N′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipy)2(Bi2Cl10)·2H2O (1) (bipy = bipyridine), with the N,N′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipy2+ moiety obtained in situ, has been synthesized under solvothermal conditions and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 is characterized by an isolated structure, consisting of N,N′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipy2+ cations, Bi2Cl104– anions and lattice water molecules. Photoluminescence experiments with solid-state samples discover that compound 1 exhibits a strong emission in the green region. Time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculation reveals that the essence of the photoluminescence of 1 can be assigned to the combination of the metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) (from the HOMO of the bismuth ion to the LUMO of the N,N′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipy2+ moiety) and the ligand-to-ligand charge transfer (LLCT) (from the HOMO of the chloride ions to the LUMO of the N,N′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipy2+ moiety).
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
