Crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and computational studies of thiazolidin-4-one derivative: (Z)-5-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-3-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2362Keywords:
Structure, thiazolidin-4-one, theoretical calculations, Intermolecular interactions, Hirshfeld SurfaceAbstract
The title compound (Z)-5-(4-chlorobenzylidene)-3-(2-ethoxyphenyl)-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one, called (CBBTZ) was characterized by X-ray single crystal diffraction, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra. The compound crystallizes in the triclinic space group P-1 with the following cell parameters: a = 9.2171(19), b = 8.4612(7), c = 11.935(3) Å, a = 101.623(11)°, β = 90.89(2)°, g = 118.148 (9)°, V = 797.3(3) Å3 and Z = 2. A data set of 2591 observed reflections were used in the refinement leading to a structure with a refinement factor of 0.05. Theoretical investigations were carried out using HF and DFT levels of theory at 6-31G(d,p) basis set. The X-ray structure is compared with that computed. The calculated geometrical parameters are in good agreement with those determined by X-ray diffraction. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 16.89(5)° indicating that the structure is non planar. The molecule exhibits intra- and intermolecular contacts of type C–H⋅⋅⋅O, C–H⋅⋅⋅S and C–H⋅⋅⋅Cl. The intercontacts in crystal structure are explored using Hirshfeld Surfaces analysis method.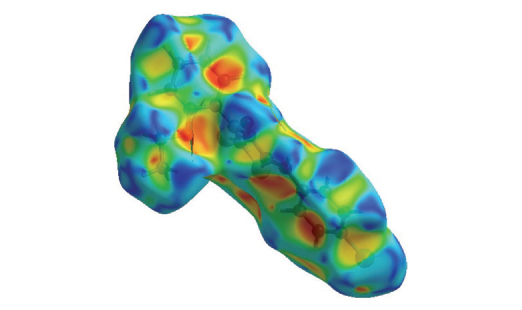
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
20.07.2016
Issue
Section
Organic chemistry
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
