Chemiluminescence Determination of Local Anaesthetic Mepivacaine in Human Plasma and Pharmaceuticals
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2015.2161Keywords:
Chemiluminescence, Mepivacaine, Local Anaesthetic, Injections, Plasma, Time ResolveAbstract
In this study, a new method has been developed for the simple determination of mepivacaine (carbocaine). The method is based on the enhancement effect of mepivacaine in the chemiluminescence (CL) reaction of tris(1,10 phenanthroline)ruthenium(II) with cerium(IV). A mechanism for the CL reaction has been proposed on the basis of UV-Vis, fluorescent and CL spectra. Under optimum conditions, the CL intensity was proportional to the concentration of the drug in solution over the range 0.45-226.25 µg mL-1 (R2=0.9996). The limit of detection (LOD) (S/N=3) was 0.34 µg mL-1. LOD was about 10 times lower than the therapeutic concentration of mepivacaine. The percent of relative standard deviation for determination of 11 replicates at level of 9.05 μg mL-1 and 90.50 μg mL-1 of mepivacaine were 1.8 and 3.7%, respectively. The proposed method was applied successfully for the determination of mepivacaine in human plasma and injectable solutions.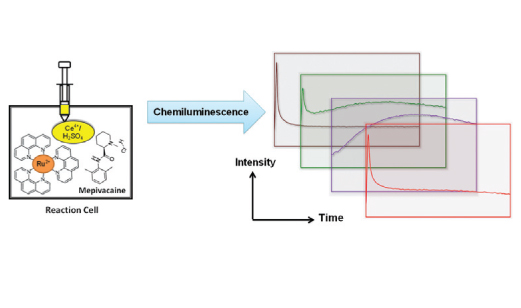
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
07.10.2016
Issue
Section
Analytical chemistry
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
