Simple, rapid and selective chronopotentiometric method for the determination of riboflavin in pharmaceutical preparations using a glassy carbon electrode
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2015.1745Keywords:
Riboflavin, chronopotentiometry, glassy carbon electrode, pharmaceutical preparationsAbstract
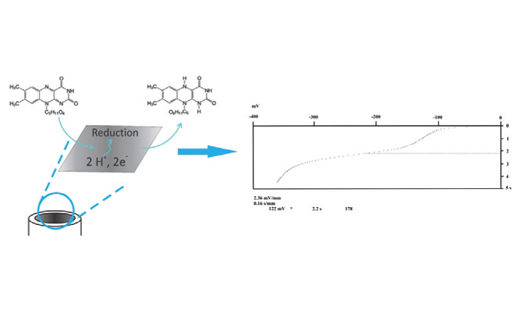
A novel, simple, sensitive and reliable electrochemical method for the riboflavin determination using chronopotentiomery with glassy carbon electrode was developed. The most important instrumental parameters of chronopotentiometry including type and concentration of supporting electrolyte, initial potential and current range were examined and optimised in respect to riboflavin analytical signal. Riboflavin provided well defined reduction signal at -0.12 V vs. Ag/AgCl (3.5 mol/L KCl) electrode in 0.025 mol/L HCl. Under optimal conditions, linear response of riboflavin was observed in the concentration range of 0.2 - 70 mg/L with achieved limit of detection of 0.076 mg/L and limit of quantitation of 0.23 mg/L of riboflavin. Common vitamins and filing materials did not interfere in the determination. The proposed method was successfully applied for determination of riboflavin in commercially available pharmaceutical preparations. The obtained results were in statistical agreement to the contents declared by manufacturer and to those obtained by HPLC used as comparative method.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
