Bioacid Hydroconversion over Co, Ni, Cu Mono- and Indium-doped Bimetallic Catalysts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2014.1135Keywords:
Carboxylic acids, hydroconversion, alcohols, indium dopingAbstract
Caprylic acid (CA) as model reactant was selectively reduced in a flow-through reactor in hydrogen stream at 21 bar total pressure and 240-360 °C over alumina loaded with the adjacent Co, Ni, Cu host and In guest metals. The main target of this research is the recognition of efficient cobalt catalysts for carboxylic group hydroconversion compared to more familiar nickel and copper composites. The catalysts were activated in H2 flow at 21 bar and 450 °C. By variation of main metal or modification with indium, mono- or bimetallic catalysts can be obtained with low hydrodecarbonylation activity and high alcohol selectivity. These composites have higher hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) activity and alcohol selectivity than the conventional commercial catalysts applied for fatty alcohol production. Great variety of catalytic behavior indicates complexity of the surface reactions determined by several interacting factors.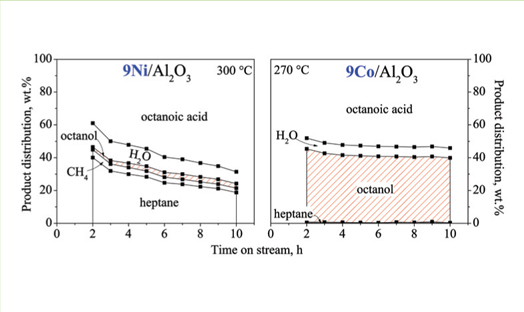
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
06.02.2015
Issue
Section
Physical chemistry
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
