N-Substituted Indole-2 and 3-Carboxamide Derivatives as Inhibitors of Human Protein Kinase CK2: In Vitro Assay and Molecular Modelling Study
Keywords:
Casein Kinase-2, Indole derivatives, Inhibitors, DockingAbstract
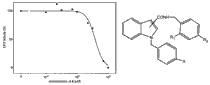
Protein kinase CK2 (Casein Kinase 2) is involved in cell growth; proliferation and suppression of apoptosis. Hence, it strongly promotes cell survival and can be considered an important target for human cancers. In the present study, a series of N-substituted indole-2- and 3-carboxamide derivatives were tested for inhibitions of human recombinant protein kinase CK2 to evaluate their anticancer properties. The inhibition test revealed that the most active compound 4 (1-benzyl- N-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamide) showed an IC50 value of 14.6 μM towards human protein kinase CK2. A molecular docking study of the compounds with CK2 was performed and revealed the binding mode of the most active compound 4, underlying its inhibitory activity.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
