Chemical Stability and Dissolution of Paracetamol Tablets Formulated by Direct Compression and Granulation Process
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2025.9374Abstract
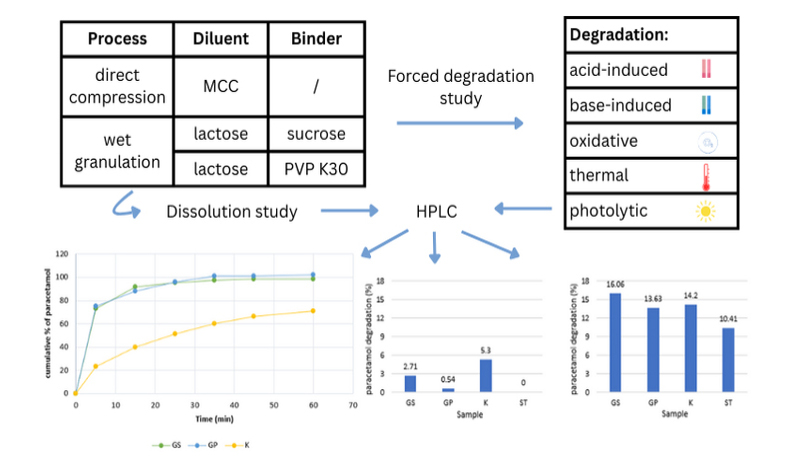
The chemical stability of active substances affects the safety and efficacy of the drug products. The aim of this study was to investigate the stability and dissolution of paracetamol tablets produced by wet granulation (GS, GP) and direct compression (K). The highest percentage of loss was observed during alkaline hydrolysis (between 10.41% and 16.06%). Acidic conditions caused the highest degradation in sample K (5.3%). Oxidative conditions lead to the highest degradation in two formulations (K, GP). The loss was below 5% after thermal and photolytic degradation for all samples, with the highest decrease found in pure paracetamol after thermal degradation (2.63%). The dissolution profiles best fit to Korsmeyer-Peppas model, with the slowest release observed in formulation K. The study of different formulations revealed a significant influence of formulation factors (producing method, presence of excipients) on the stability and dissolution of paracetamol.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nemanja Todorović, Darija Sazdanić, Bojana Mamužić, Mladena Lalić-Popović, Milica Atanacković Krstonošić, Mira Mikulić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
