Synthesis and Biological Activity of Some Novel Quinolinones Derived from 1-Ethyl-1,2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxoquinoline-3-carbaldehyde
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2025.9335Abstract
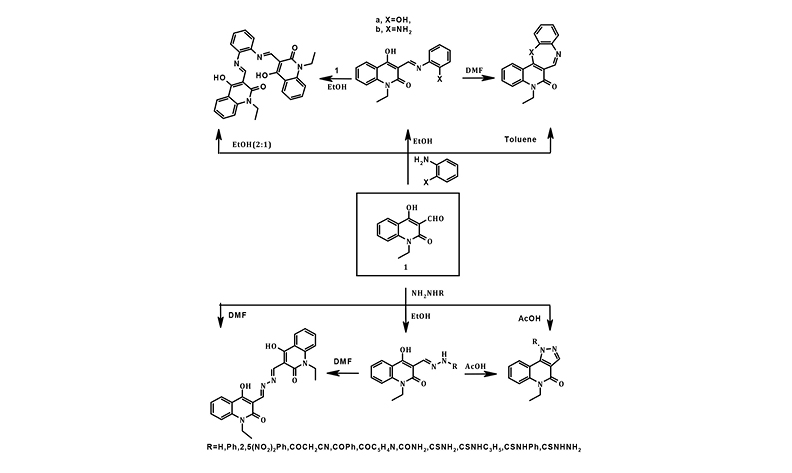
The reactivity of 1-ethyl-1,2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxoquinoline-3-carbaldehyde (1) towards some diaza-nucleophiles has been investigated, under various reaction conditions. 1-Ethyl-1,2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxoquinoline-3-carbaldehyde (1) was reacted with hydrazine, phenylhydrazine, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, acid hydrazides, semicarbazide, thiosemicarbazides, thiocarbohydrazide, ortho-phenylenediamine and ortho-aminophenol. It was found that solvents used in these reactions impacted product selectivity. Accordingly, these reactions led to various open-chain and/or cyclic derivatives of quinolinone. The structure of the new compounds was determined using spectroscopic techniques and elemental analyses. All products were screened in vitro to determine their antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activities. Compounds 2a and 2c are the most active compounds against bacterial and fungal strains. While the most effective compounds against breast cancer (MCF-7) are compounds 2a and 8a.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatma Youssef, Mostafa Ismail, prof, Heba Hassan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
