Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties of L-Cysteine-Mediated Self-Assembled Au-Ag/AgCl Nanoparticles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2025.9185Abstract
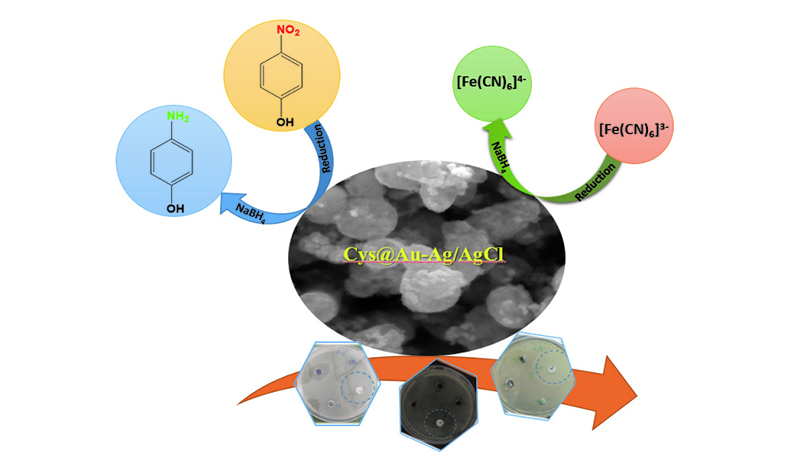
In this study, the self-assembly of gold and silver-based nanoclusters modified by L-cysteine (Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl) was prepared using a simple and straightforward hydrothermal method. Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl exhibited efficient catalytic activity for the rapid reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to the less toxic 4-aminophenol (4-AP) in the presence of NaBH4 as a reducing agent, completing the reaction within a few minutes with a rate constant of 6.1 × 10−3 s−1. The catalytic performance of Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl was optimized by studying the effect of various parameters on the catalytic reduction. In addition, Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl nanocomposite was used for catalytic reduction of K3[Fe(CN)6] in the presence of NaBH4, and the reaction rate constant was found to be 1.73 × 10−2 s−1. The antibacterial activity of Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl nanocomposite was also evaluated against common drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative bacteria (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli). The results demonstrated that the multifunctional Cys@Au-Ag/AgCl nanocomposite exhibited good antibacterial activity against these clinical drug-resistant bacteria.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Moein Rezazadeh, Zeinab Moradi Shoeili

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
