Phytochemical composition, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory effects of Stahlianthus thorelii Gagnep. rhizomes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.9043Abstract
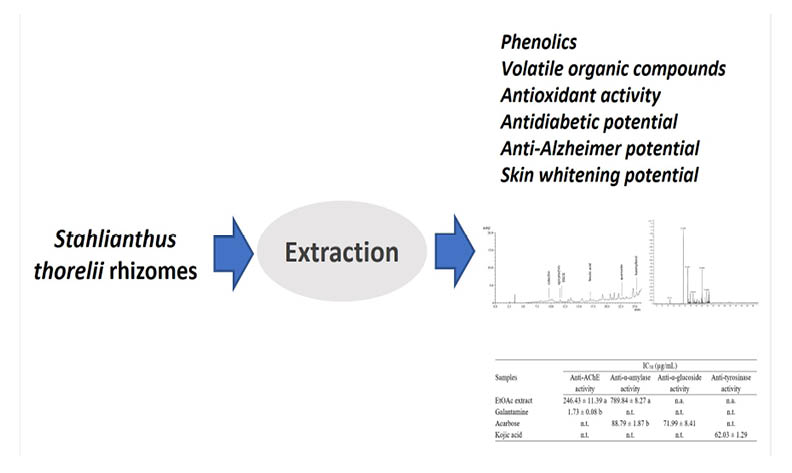
Stahlianthus thorelii Gagnep. is used in traditional medicine to treat various diseases. In this study, ethyl acetate (EtOAc) extract of S. thorelii rhizomes was analyzed for its phychemicals, antioxidant activity and inhibition against enzymes (acetylcholinesterase, α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and tyrosinase). The EtOAc extract showed the presence of ferulic acid, catechin, epicatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, quercetin, and kaempferol, with average levels ranging from 169.29 to 2449.60 μg/g. Analysis of the volatile components of the extract revealed that β-patchoulene (23.1%), (E)-nerolidyl isobutyrate (11.9%), and aristolene (10.8%) were the major compounds. The antioxidant potential of the extract measured by DPPH (IC50 = 86.94 ± 2.87 μg/mL) and ABTS (IC50 = 743.60 ± 56.52 μg/mL) assays showed promising results. The inhibitory effects against acetylcholinesterase and α-amylase demonstrated potential with IC50 values of 246.43 ± 11.39 and 789.84 ± 8.27 µg/mL, respectively. The findings above suggest that the EtOAc extract of S. thorelii could contribute to supporting the treatment of certain diseases such as diabetes and Alzheimer's.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Pham M. Tuan, Danh C. Vu, Sy Vo Van, Ngo Thi Thuy, Vo Mong Tham, Nguyen Ngan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
