Effect of Biphenyl Derivative of Coumarin Compounds Photodynamic Therapy on The Expression of Carcinoma-Associated Genes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8948Abstract
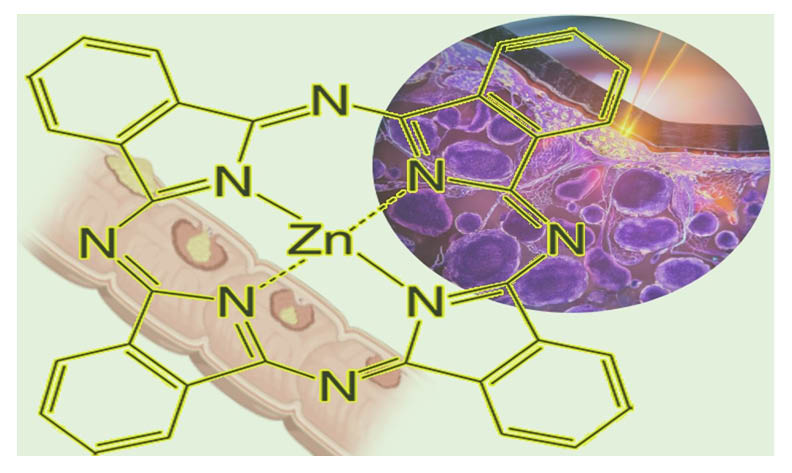
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a cancer treatment. Singlet oxygen is produced as a result of the photochemical reaction between light, photosensitizer (PS), and molecular oxygen, which kills cells. Colon cancer, affecting 1.23 million people worldwide, often requires surgery but has high recurrence and metastasis rates. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an alternative treatment for colon cancer. This study used MTT assays to evaluate cell viability and applied Zinc(II) Phthalocyanine photosensitizers to the colorectal adenocarcinoma (HT-29) cell line to investigate cancer pathways via flow cytometry and q-PCR. The results showed that PDT with Zinc(II) Phthalocyanine significantly reduced cell viability in HT-29 cells and induced apoptosis at a rate of 53%. According to q-PCR results, CT values of ten out of thirty genes were found to be significant and their association with cancer was evaluated.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Asiye Yurttaş, Tuğba Elgün, Burçin Erkal Çam, Melike Kefeli, Kamil Çınar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
