Electrochemical Sensors for Bisphenol A Analysis in Foods and Beverages — A New Approach in Food Quality Control
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8918Abstract
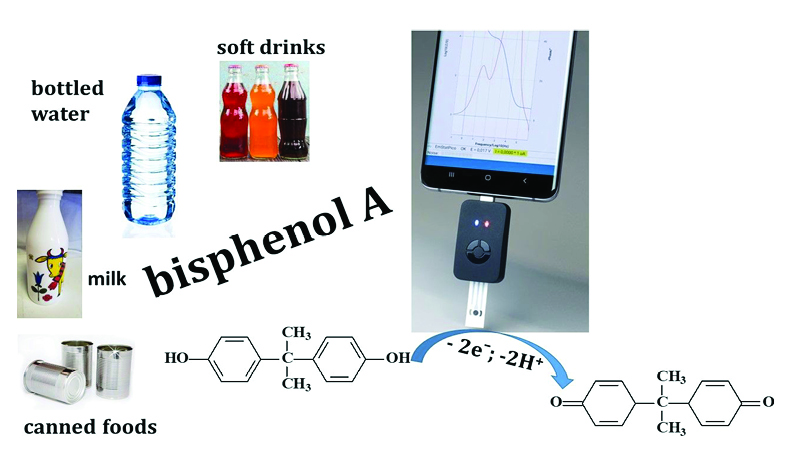
Modern nanofabrication technologies combined with electrochemical techniques offer benefits in terms of extremely high sensitivity, low limit of detection, minimum power requirement, simplicity, and low cost of the electrochemical sensors making them powerful for food quality evaluation. The limited number of electrochemical non-enzymatic sensing platforms for bisphenol A (BPA) successfully applied for safety assessment of foods and beverages, testifies that the food matrices present significant challenges and there is still a need to improve the analytical performances of these devices. This review systematically explores the contributions of diverse functional nanomaterials, metal–organic frameworks, ionic liquids, and molecular imprinting in improving the sensor performance. A critical discussion on the latest interesting innovations and most promising electrochemical tools for BPA analysis is presented. By addressing the electrochemical aspects and challenges in the design of BPA sensors and exploring innovative solutions, the article offers insights into future prospects and avenues, paving the way for advancements in this field.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Totka Dodevska

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
