Insights into Antiradical Behavior: Crystal Structures and DFT Analysis of 2-Formylpyridine N4-Allylthiosemicarbazone Salts
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8728Abstract
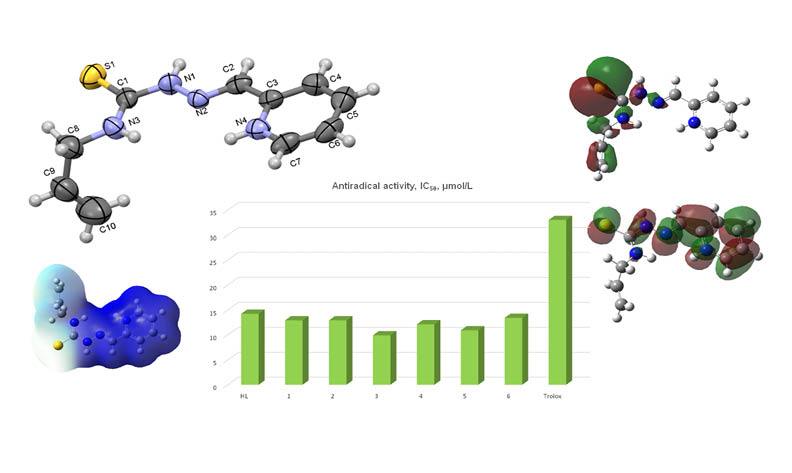
In this paper, six new salts of 2-formylpyridine N4-allylthiosemicarbazone ([H2L]X⸱nH2O, where X is NO3- (1), NH2SO3- (2), Cl- (3), Cl3CCOO- (4), Cl2CHCOO- (5), ClCH2COO- (6); n = 0 (1, 3, 5, 6), 1 (2, 4)) were synthesized and physico-chemically characterized by elemental analysis, molar conductivity measurements, FT-IR studies, 1H and 13C NMR. The crystal structures of compounds 1-5 were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Analysis of crystal data shows that the structures of these compounds consist of protonated thiosemicarbazone H2L+, anions of acid residue and water molecules in 2 and 4. These compounds manifest antiradical activity toward ABTS•+ cation radicals that exceeds the activity of non-protonated thiosemicarbazone HL and trolox, that is used in medicine. The most active one is compound [H2L]Cl (3) with IC50 value 9.9 μmol/L. Density Functional Theory calculations showed that the electronic structure of cation H2L+ is more favorable for electron acceptation if compared with HL.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yurii Chumakov, Vasilii Graur, Ianina Graur, Victor Tsapkov, Olga Garbuz, Aurelian Gulea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
