Synthesis of Schiff Bases of Usnic Acid and Investigation of Their Antidiabetic, Antidepressant, Anti-Parkinson’s, Neuroprotective and Antioxidant Potentials
Biological activities of usnic acid Schiff base derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8703Abstract
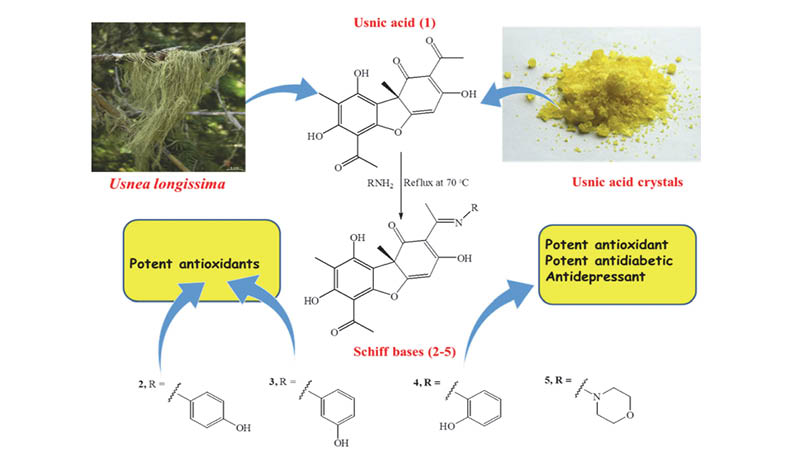
Schiff bases have various pharmacological activities due to the azomethine (-C=N-) group. Usnic acid is the most famous lichen metabolite and it contains two carbonyl groups to synthesize the Schiff base derivatives with primary amines. Therefore, in the current study, the known Schiff base derivatives (2-5) of usnic acid (1) were synthesized to explore their antidiabetic, neuroprotective, antioxidant, antidepressant and anti-Parkinson’s properties. Among the tested compounds, compound 4 exhibited the strongest antidiabetic and antidepressant activities, inhibiting α-glycosidase, α-amylase and MAO-A enzyme activities, respectively. Moreover, all of the tested compounds strongly scavenged the ABTS and DPPH radicals and the ABTS radical scavenging activities of 3 and 4 were found to be higher than the commercial antioxidants BHA and trolox. All of the tested compounds did not show any significant anti-Parkinson’s and neuroprotective activities. In conclusion, compound 4 can be suggested as a drug candidate molecule for further studies due to its strong antioxidant, antidiabetic and antidepressant properties.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Lawali Yabo Dambagi, Ahmet Cakir, Mehmet Akyuz, Ayşegül İyidogan, Ali Aslan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
