Walnut shells activated carbons for adsorption of nitrite ions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8693Abstract
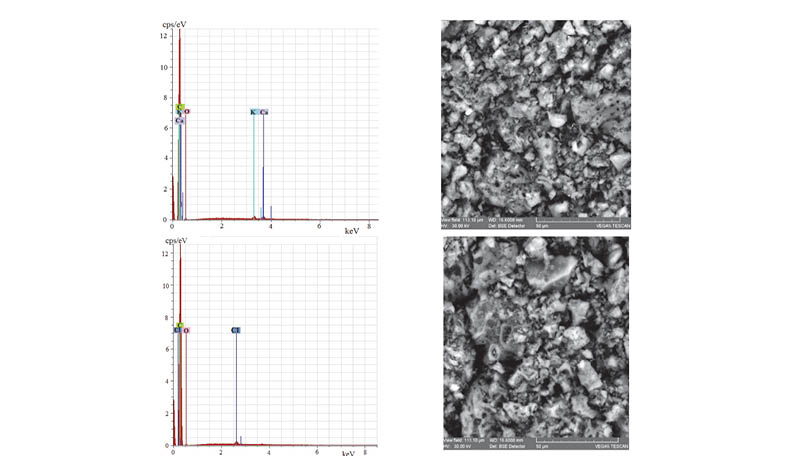
In this paper, activated carbons obtained from walnut shells were used as adsorbents to remove nitrite ions from aqueous solutions. The novel adsorbent was obtained by modification with hydrochloric acid. The physical-chemical characteristics of activated carbons were determined from nitrogen sorption isotherms, SEM-EDX, elemental analysis, FTIR, thermal analysis, and temperature programmed decomposition (TPD). According to the results obtained, chlorine is retained on the surface in an amount of 2%. The results of batch experiments indicate that maximum adsorption/ removal of nitrite ions can be achieved at pH = 3, being of 0.2 mg/g for CAN and 4.7 mg/g for CAN-Cl. To study the adsorption of nitrite ions on activated carbons the following mathematical models were used: pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and intraparticle diffusion kinetic models, and Langmuir, Freundlich, Dubinin-Radushkevich, and Temkin-Pyzhev isotherm models.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Irina Ceban (Ginsari), Raisa Nastas

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
