Elimination of Cadmium using Silica Gel Prepared from Blast Furnace Slag
Adsorption of cadmium ions by silica gel
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8692Abstract
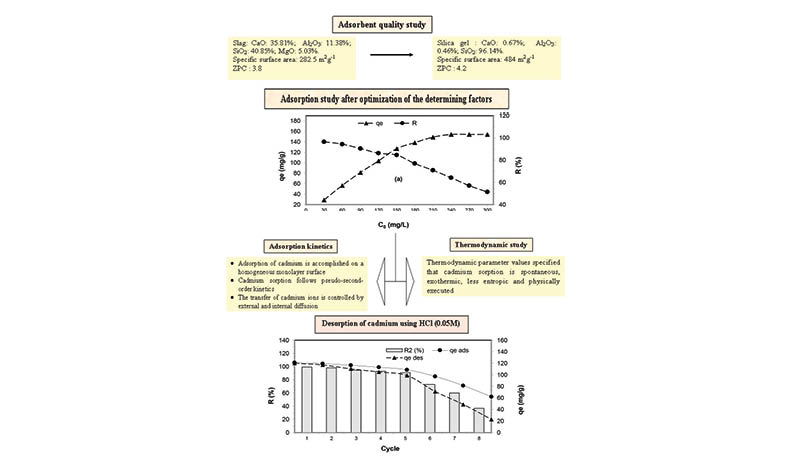
In this work, the silica gel recovered from the blast furnace slag was exploited for the elimination of cadmium in batch mode under the action of different factors. Physico-chemical analyzes revealed that the modified slag is only composed of silica (96.14%). Its specific surface area is 484 m2g-1 and the pH corresponding to PZC is 4.2. The experiment revealed that the effect of the determining factors contributed considerably to the progression of the adsorption capacity (154.11 mg/g). Adsorption isotherms demonstrated that the removal of cadmium on modified slag was accomplished on a homogeneous monolayer surface (R2= 099; qmax= 153.84 mg/g). Kinetic analysis revealed that this process agreed with the pseudo-second-order kinetic model (R2 ≥ 0.99). In addition, it was indicated that the diffusion of the pollutant is ensured by external and intraparticle diffusion. The values of thermodynamic variables clarified that cadmium sorption is spontaneous, exothermic, less entropic and physically executed under the effect of electrostatic interaction. The desorption process revealed that the reuse of Silica gel was feasible over five consecutive cycles.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Toufik Chouchane, Mohamed Tayeb Abedghars, Sabiha Chouchane, Atmane Boukari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
