Succinyl Curcumin Conjugated Chitosan Polymer-Prodrug Nanomicelles: A Potential Treatment for Type-II Diabetes in Diabetic Balb/C Mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2024.8658Abstract
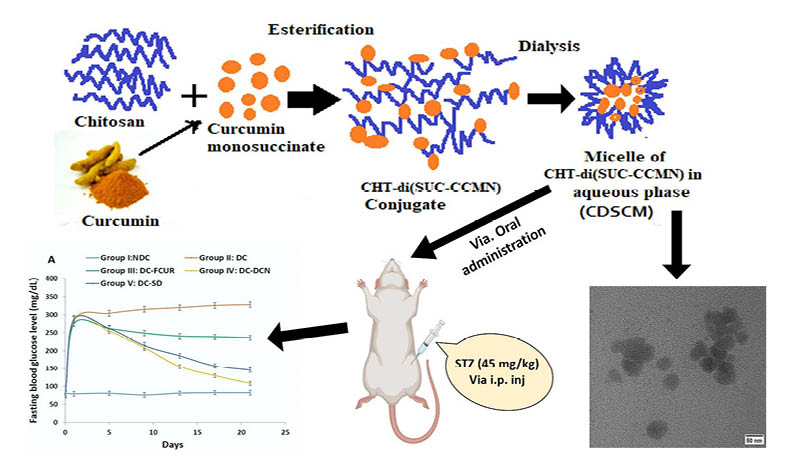
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder marked by elevated blood sugar levels, leading to organ dysfunction. Curcumin, derived from turmeric, exhibits promise in managing type II diabetes. Nanomicelles were created by conjugating curcumin with chitosan through succinic anhydride. Succinyl-curcumin, the resultant compound, was esterified with chitosan to form a polymer prodrug conjugate. Nanomicelles, formed via dialysis, were spherical with a hydrodynamic size of 49.37 nm. In vitro release studies revealed 97% curcumin release at pH 5 in 7 days. A 21-day experiment on diabetic mice compared nanomicelles, standard drug, and free curcumin's impact on fasting blood glucose. The study showcased gradual, controlled curcumin release from nanomicelles, suggesting their potential in type II diabetes treatment.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rahaman Sk Mosiur, Gouranga Dutta, Ranu Biswas, Abimanyu Sugumaran, Mohamed M. Salem, Mohammed Gamal, Mohamed AbdElrahman, Mounir M. Salem-Bekhit

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
