Effects of the extraction conditions on functional and structural characteristics of proteins from fenugreek seeds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8576Abstract
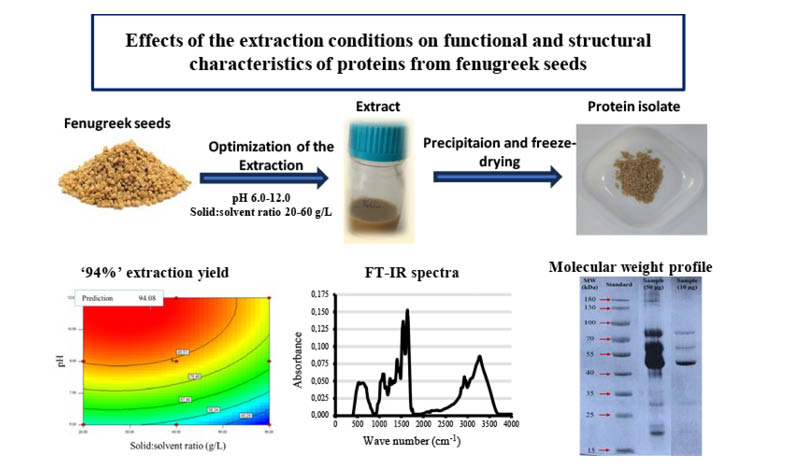
The aim of this study is to optimize the extraction process and characterize the proteins found in fenugreek seeds. The water and oil holding capacities, coagulated protein content, foaming and emulsification properties of the isolated proteins at all extraction conditions were investigated. Also, solubility, molecular weights, structural and thermal properties were determined. In the extraction processes carried out at different pHs (pH 6.0-12.0) and solid:solvent ratios (20-60 g/L), it was determined that the highest extraction yield (94.3±0.3%) was achieved when the pH was 11.47 and the solid-solvent ratio was 34.50 g/L. Three distinct bands (46, 59 and 80 kDa) in the range of 22-175 kDa were determined for the fenugreek seed protein isolate obtained at optimum extraction conditions. Protein secondary structures were achieved using Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectra and it was determined that β-sheet structures were highly present. In addition, denaturation temperatures and denaturation enthalpy were calculated as ~119°C and 28 mJ/g, respectively.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Hilal Isleroglu, Gamze Nur Olgun

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
