Insight into the interaction of quinizarin with SDS micelles – effects of additives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8539Abstract
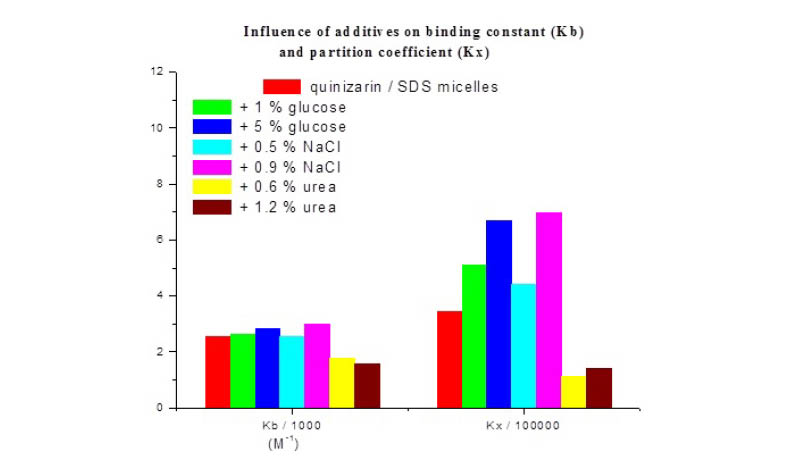
Association behavior between quinizarin (1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone), an analogue of the chromophore of anthracycline anticancer drugs and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) micelles in the presence of glucose, NaCl and urea additives was studied using absorption spectroscopy and conductometric techniques. The spectral results indicate an increase of binding constant and partition coefficient values in the presence of glucose and NaCl whereas the addition of urea leads to a decrease of binding strength and quinizarin partitioning into SDS micelles. Thus, the rise of NaCl and glucose concentrations is favorable for the quinizarin distribution into SDS micelles. From electrical conductivity measurements it was found that the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of SDS/quinizarin system decreases by adding NaCl and glucose whereas urea has not influence on the micelization process at the concentrations used in the present study. Since biologically compounds like glucose, NaCl and urea are found in the human body, the attained outcomes can be important in finding of effective drug delivery systems.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ana Maria Toader, Petruta Oancea, Izabella Dascalu, Mirela Enache

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
