Quality by Design based development of electrospun nanofibrous solid dispersion mats for oral delivery of efavirenz
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8538Abstract
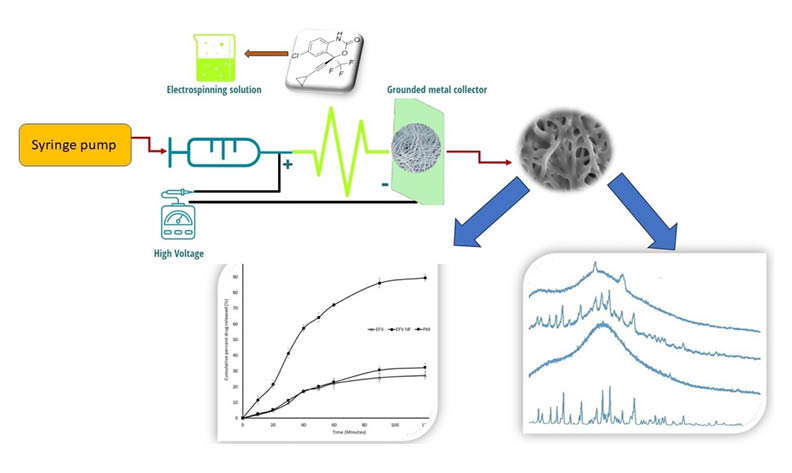
Poor aqueous solubility often results in poor dissolution behavior and, consequently, poor bioavailability for those drugs whose intestinal absorption is dissolution rate limited. It is essential for formulation scientists to identify strategies to improve the solubility and dissolution rate of candidate drugs in order to improve their bioavailability. The present study investigated electrospun polymeric nanofibers for efavirenz, a Class II drug in the Biopharmaceutical Classification System. In order to fabricate nanofibers, hydrophilic spinnable polymer like Soluplus was used. Statistical design of experiments was used to optimize electrospinning parameters. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) studies confirmed the presence of nanofibrous material in the mat. The x-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies advocated the amorphization of efavirenz in the nanofiber samples. The nanofiber-based platform significantly improved in vitro dissolution of efavirenz compared to pure efavirenz crystals.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Md. Faseehuddin Ahmed, Kalpana Swain, Satyanarayan Pattnaik, Biplab Kumar Dey

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
