Modification of PVA Nanofiber by Simple Hot Water Treatment and Application on the Removal of Malachite Green Dye From Aqueous Solutions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8501Abstract
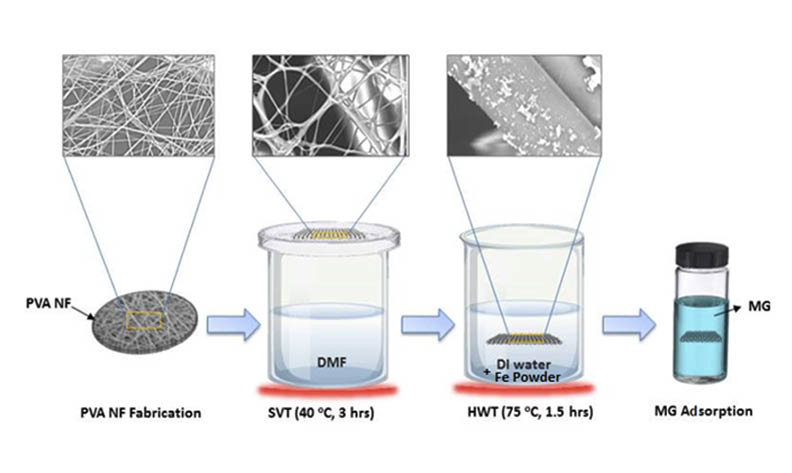
In this study, the crosslinking of PVA nanofiber was increased using solvent vapor treatment. Then, Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized by a simple hot water technique and composited with the nanofiber. The study focuses on applying the modified PVA nanofibers to remove malachite green (MG) from water using different pH, contact times, and dye initial concentrations. The surface morphology of the nanofiber was determined using SEM, FTIR, and XRD techniques. SEM showed that the crosslinking was increased, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles appeared as agglomerates on the surface of the nanofiber. The removal percentages at optimal pH and contact time were 99.76%, and 99.5%, respectively. Thereafter, kinetics was studied by the linear pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, Elovich equation, and Intraparticle diffusion models. Results demonstrated that the adsorption kinetics follow the pseudo-second order. Moreover, the adsorption isotherm was discussed using Langmuir and Freundlich equations. The Langmuir equation best described the adsorption with R2 value of 0.9771, and the maximum removal was 128.205 mg/g. As a result, the MG dye molecules covered the PVA nanofiber/Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a monolayer and homogenous coverage. The results of this study are significant
for industries’ wastewater treatment as they provide a potential solution for the removal of MG dye from textile, paper, cosmetics, food, and aquaculture industries’ wastewater.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Banaz Arshad Abdulghafar, Suhad A. Yasin; Nawzad S. Saadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
