Synthesis, Characterization and X-Ray Crystal Structures of Oxidovanadium(V) Complexes Derived from N’-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)-4-methylbenzohydrazide with Antibacterial Activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8347Abstract
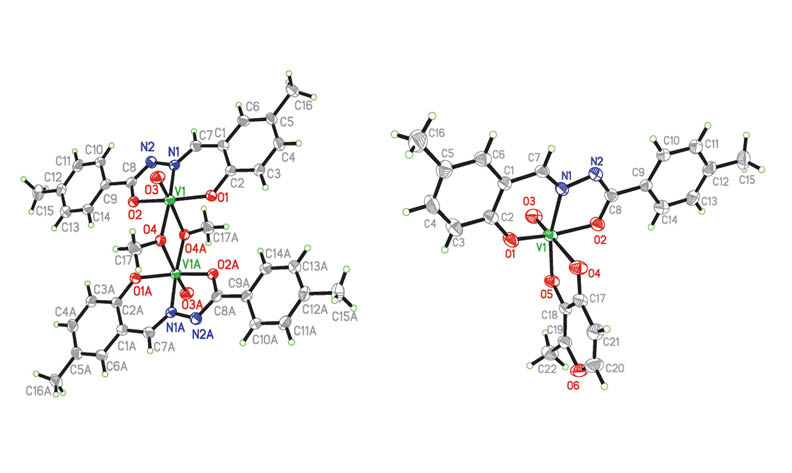
A dinuclear oxidovanadium(V) complex [V2O2L2(OMe)2] (1) was synthesized from N’-(2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)-4-methylbenzohydrazide (H2L) and VO(acac)2 in MeOH. Reaction of complex 1 with 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone (HL’) afforded a mononuclear oxidovanadium(V) complex [VOLL’] (2). The hydrazone and both complexes were characterized by IR, UV and 1H NMR spectroscopy, as well as X-ray single crystal determination. X-ray powder diffraction of the complexes was performed. The V atoms in the two complexes are in octahedral coordination. The molecules of complex 2 are linked through non-classical hydrogen bonds of type C–H∙∙∙O to form one-dimensional chains running along the a axis. The biological assay indicates that the complexes have good antimicrobial activities on the bacteria strains P. aeroginosa, S. aureus, B. subtilis and E. coli.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 1970 Xue-Rong Tan, Wei Li, Meng-Meng Duan, Zhonglu You

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
