Investigating the Polyphenolic Profile and the Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity of Tarragon (Artemisia dracunculus L) cultivated in Central Romania
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2023.8225Abstract
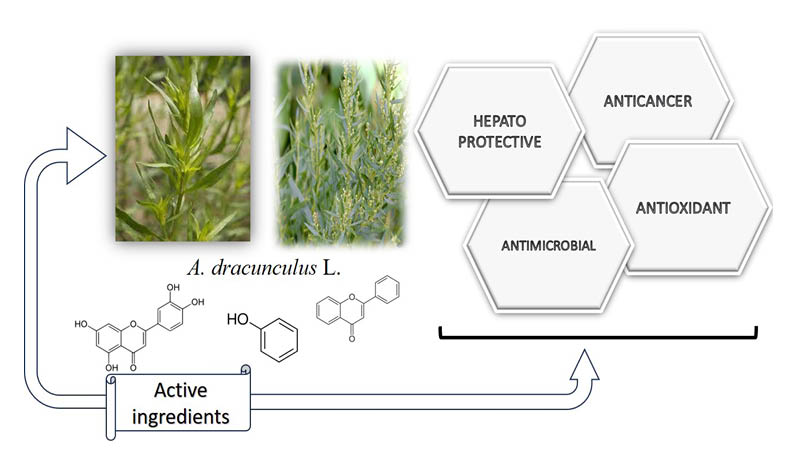
The chemical composition, as well as the antioxidant and antibacterial properties of Artemisia dracunculus L. leaves were studied using four types of solvents for extraction., i.e. ultrapure water, ethanol, methanol and acetic acid. The values reached for total polyphenols (determined by the Folin Ciocâlteu method) were between 77.28±1.48 mg GAE/g d.w. - 192.14±5.33 mg GAE/g d.w. and 46.45±0.11 mg QE/g d.w. - 126.45±0.32 mg QE/g d.w. Antioxidant activity (DPPH) was recorded via IC50 levels between 14.66±0.3 μg/mL and 20.33±0.2 μg/mL. The phenolic compounds, such as flavonoids, coumarins, phenolic acids, were identified using the HPLC method. We analysed the antibacterial activity of the extracts, and the most resistant bacteria were Escherichia coli 29 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa 323 with MIC levels at ≥ 1000µg/mL. Methanolic extracts were the strongest. Artemisia dracunculus L. leaf extracts contain a significant variety of beneficial active chemical and biological compounds, thus the plant is recommended both for culinary and medicinal purposes.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 1970 Ramona Cristea, Daniela Maria Sandru

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
