Comparative Molecular Field Analysis (CoMFA), Molecular 1 Docking And ADMET Study on Thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid 2 Derivatives as New Neuraminidase Inhibitors
Keywords:
thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, Neuraminidase, influenza, 3D QSAR, CoMFA, 29 Molecular Docking, ADMET study.Abstract
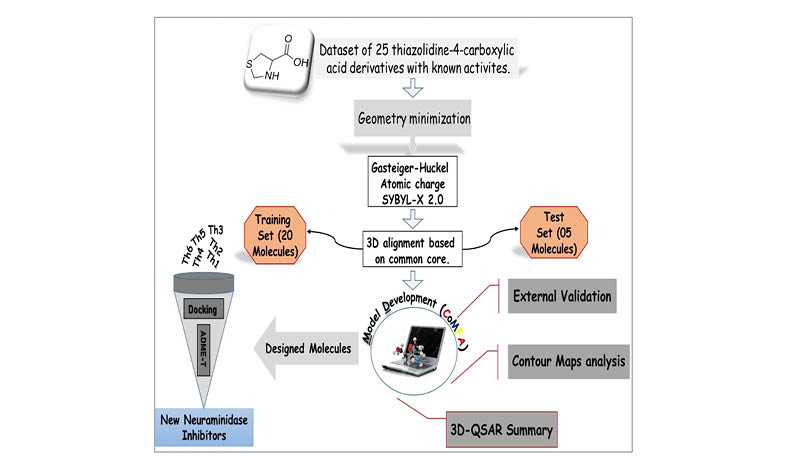
The objective of this research was to create a 3D-QSAR CoMFA model for a set of twenty-five neuraminidase inhibitors containing thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid derivatives and to identify a new potent neuraminidase inhibitor for the treatment of influenza. The generated model has excellent statistical parameters: Q2 = 0.708, R2 = 0.997. External validation results were (r20 = 0.922, K= 1.016, R2pred = 0.674, r2m= 0.778) indicating the good predictive power of the constructed model. Based on the contour map of the CoMFA model, we were able to propose six novel compounds with higher Neuraminidase inhibitory activity than the most active compound. The six proposed molecules were submitted to molecular docking to analyse the bindings formed between the newly designed molecules and the Neuraminidase. We observed that all of the proposed molecules are more stable on the active site of Neuraminidase than the reference molecule. A reaction mechanism was also described for synthesizing the six proposed compounds, which could potentially be explored further in the hunt for novel neuraminidase inhibitors. In conclusion, this work has identified potential candidates for the development of more effective neuraminidase inhibitors for the treatment of influenza.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 1970 OUASSAF MEBARKA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
