Physico-chemical properties of lomefloxacin, levofloxacin and moxifloxacin relevant to Biopharmaceutics Classification System
Keywords:
Fluoroquinolones, Bioavailability, Molecular modeling, BCSAbstract
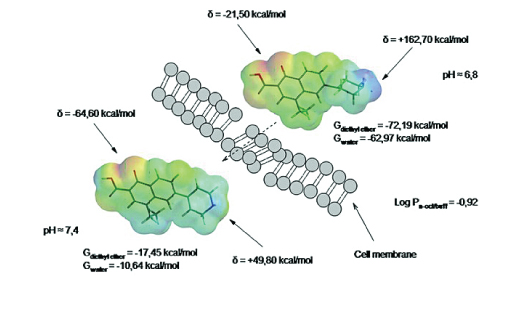
The aim of this investigation was to identify by in silico and in vitro methods the physico-chemical properties impact on bioavailability of three fluoroquinolones second, third and fourth generation in relation to Biopharmaceutics Classification System. These properties were estimated by analysis of the electrostatic potential pattern and values of the free energy of solvation as well as the distribution coefficients and true partition coefficients of the studied compounds. The study was based on theoretical quantum-chemical methods and in vitro shake-flask technique with two immiscible phases, n-octanol and phosphate buffer and as well experimental potentiometric method to estimate protonation macro- and microconstants. Properties identified in the in vitro and in silico studies were similar and indicated high lipophilic properties of molecules and, also their good solubility in a polar medium. It appears that the theoretical methods and simple in vitro studies are useful tools for predicting the bioavailability of medicinal substances based on the Biopharmaceutics Classification System principles.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
