Application of Carrier Element Free Coprecipitation (CEFC) Method for Determination of Co(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) Ions in Food and Water Samples
Keywords:
Heavy metals, separation, preconcentration, carrier element free coprecipitation, flame atomic absorption spectrometryAbstract
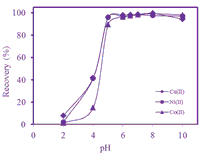
A simple and highly sensitive separation and preconcentration procedure, which has minimal impact on the environment, has been developed. The procedure is based on the carrier element free coprecipitation (CEFC) of Co(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) ions by using 2-{4-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]-3-(4-methylbenzyl)-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro- 1H-1,2,4-triazol-l-yl}-N'-(pyridin-2-yl methylidene)acetohydrazide (IMOTPA), as an organic coprecipitant. The levels of analyte ions were determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). The detection limits for Co(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions were found to be 0.40, 0.16 and 0.17 microg L(-1), respectively, and the relative standard deviations for the analyte ions were lower than 3.0%. Spike tests and certified reference material analyses were performed to validate the method. The method was successfully applied for the determination of Co(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions levels in sea and stream water as liquid samples and red pepper, black pepper, and peppermint as solid samples.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
