Theoretical analysis of the mechanism and regioselectivity of the 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition of E-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(10H-phenothiazin-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one with some nitrilimines using DFT and the distortion/interaction model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2014.305Keywords:
Regioselectivity, Cycloaddition, Density functional calculations, Distortion/interaction modelAbstract
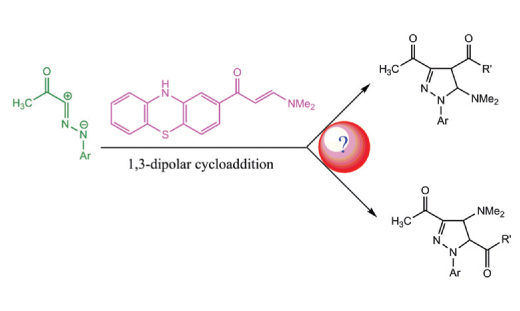
The regiochemistry of 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of E-3-(dimethylamino)-1-(10H-phenothiazin-2-yl) prop-2-en-1-one with some nitrilimines were investigated using density functional theory (DFT) -based reactivity indexes, activation energy calculations and the distortion/interaction model at B3LYP/6-311G(d,p) level of theory. Analysis of the geometries and bond orders (BOs) at the TS structures associated with the different reaction pathways shows that these 1,3- dipolar cycloaddition reactions occur via an asynchronous concerted mechanism. Analysis of the local electrophilicity and nucleophilicity indexes and distortion/interaction energies allows an interpretation about the regioselectivity of these 1,3- dipolar cycloaddition reactions. The theoretical results obtained in the work clearly predict the regiochemistry of the isolated cycloadducts and agree to experimental results.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
