Synthesis, Characterization and DNA Cleaving Studies of New Organocobaloxime Derivatives
Keywords:
Organocobaloxime, BF2 bridged, trinuclear, DNA cleavage, by thermalAbstract
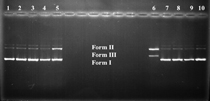
Dioxime ligand (H2L) was synthesized by condensation reaction between 4-biphenylchloroglyoxime and 4-chloroaniline. The metal complexes of the types, [Co(HL)2(i-Pr)Py], [CoL2(i-Pr)PyB2F4] and [CoL2(i-Pr)Py(Cu(phen))2](ClO4)2 [H2L = 4-(4-chlorophenylamino)biphenylglyoxime; phen = 1,10-phenanthroline; i-Pr = isopropyl; Py = pyridine] were synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR, 1H NMR and magnetic susceptibility, conductivity measurements. The results of elemental analyses, IR and NMR confirmed the stoichiometry of the complexes and the formation of ligand frameworks around the metal ions. The magnetic moment measurements of the complexes indicated that the complexes are diamagnetic (low-spin d6 octahedral) except trinuclear complex. Furthermore the interaction between the dioxime ligand and its complexes with DNA has also been investigated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The trinuclear Cu2Co complex with H2O2 as a cooxidant exhibited the strongest DNA cleaving activity.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
