4-Fluoro-N’-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide and its oxidovanadium(V) complex: Syntheses, crystal structures and insulin-enhancing activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2016.2589Keywords:
Oxovanadium complex, Kojic acid, aroylhydrazone, crystal structure, insulin-enhancing activityAbstract
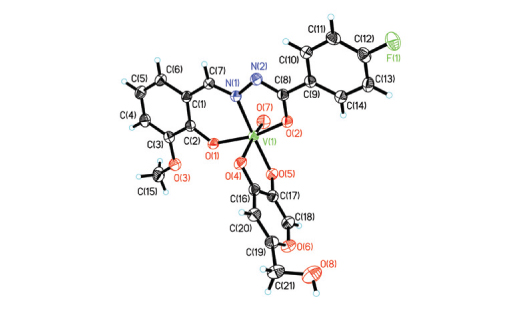
A hydrated hydrazone compound, 4-fluoro-N'-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)benzohydrazide monohydrate (H2L·H2O), was prepared and characterized by elemental analysis, HRMS, IR, UV-Vis and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Reaction of H2L, kojic acid (5-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4H-pyran-4-one; Hka) and VO(acac)2 in methanol afforded a novel oxidovanadium(V) complex, [VO(ka)L]. The complex was characterized by elemental analysis, IR, UV-Vis and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Thermal analysis was also performed. Structures of H2L and the complex were further confirmed by single crystal structural X-ray diffraction. The vanadium complex is the first structurally characterized vanadium complex of kojic acid. Insulin-mimetic tests on C2C12 muscle cells indicate that the complex significantly stimulated cell glucose utilization with cytotoxicity at 0.11 g L–1.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
