Computer Simulation of Speciation of Trivalent Aluminum, Gadolinium and Yttrium Ions in Human Blood Plasma
Keywords:
Aluminum, gadolinium, yttrium, speciation, blood plasmaAbstract
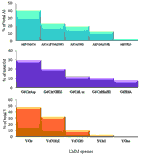
The speciation of Al3+, Gd3+ and Y3+ ions in human plasma has been studied by computer simulation using the program HySS2009. A literature computer model of blood plasma was updated and comprised 9 metals, 43 ligands and over 6100 complexes. To this model critically evaluated data of Al3+, Gd3+ and Y3+ constants with blood plasma ligands have been added. Low molecular mass (LMM) speciation of Al3+ ion strongly depends upon the chosen equilibrium model of the metal – phosphate and metal – citrate systems. The obtained computer simulation of LMM speciation data of Al3+ ion were: AlPO4Cit (40.7%), AlPO4CitOH (22.9%), AlCitOH (19.2%) and AlPO4(OH) (12.7%) (% of total LMM Al species pool); for Gd3+ ion: GdAspCit (30%) and GdCit(OH)2 (20%) (% of total [Gd]) and for Y3+ ion: YCit (48%), Y(CO3)2 (32%) and Y(CO3) (11%) (% of total [Y]). Citrate appears as the important binding and mobilizing ligand for all examined ions, while the dominating species are the ternary ones.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
