Theoretical Study on Stability and Spectroscopy of C84O2 Based on C84(D2d)
Keywords:
C84O2, energy gap, NICS, B3LYP/6-31G(d).Abstract
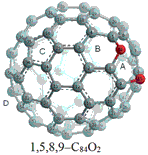
The relative stabilities of the twenty-three possible isomers for C84O2 based on C84(D(2d)) were studied by using density functional theory (DFT) at B3LYP/6-31G(d) level. The most stable isomer of C84O2 was found to be 1,5,8,9-C84O2 which contains annulene-like structures. In this isomer, two oxygen atoms are added on the same hexagon, which is called a same-ring adduct. The energy gap of C84O2 is narrower than that of C84(D(2d)). The chemical shifts of the bridged carbon atoms in C84O2 are changed upfield compared with those of the same carbon atoms in C84(D(2d)). The same-ring adduct possesses the higher aromaticity than C84(D(2d)). The area within the range of 0.2 nm from the cage center of C84(D(2d)) or C84O2 is the most suitable area for calculating NICS values.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
