New synthetic routes for the preparation of ruthenium-1,10-phenanthroline complexes. Tests of cytotoxic and antibacterial activity of selected ruthenium complexes.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2014.1130Keywords:
ruthenium complexes, phenanthroline, X-ray structure, biological activityAbstract
Three novel complexes have been prepared through reactions of precursor [(dmso)2H][trans-RuCl4(dmso-S)2] (P) and 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) at different conditions. Whereas the analogs of mer-[RuCl3(dmso-S)(phen)] (1) and [Ru(phen)3]Cl2·6CH3OH (3·6CH3OH) have already been prepared by other synthetic routes before, product (H3O)[RuCl4(phen)]·4H2O (2·4H2O) is unprecedented. In the latter, isolated from highly acidic medium, one strongly bound dmso molecule in precursor P was substituted by chloride. Biological activity of 1 and previously isolated ruthenium-purine complexes ([mer-RuCl3(dmso-S)(acv)(CH3OH)] (4) (acv = acyclovir); [trans-RuCl4(dmso-S)(guaH)] (5) (guaH = protonated guanine)) was tested and compared. These data show that compounds 1, 4 and 5 are slightly cytotoxic against B-16 malignant melanoma cells but not against non-transformed V-79 cells. It seems that coordinated phen ligand increases the cytotoxicity of 1 in comparison to ruthenium precursor. The inability of tested compounds to induce lysis of bovine erythrocytes suggests that their cytotoxic effect is not due to the membrane damage.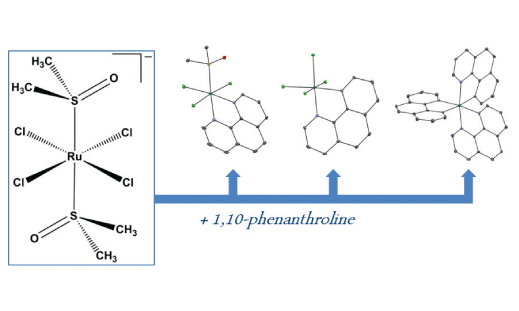
Additional Files
Published
06.02.2015
Issue
Section
Inorganic chemistry
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
