Dialkyltin(IV)bis(O–tolyl/benzyldithiocarbonate) complexes: Spectroscopic, thermogravemetric, antifungal and crystal analysis of n–Bu2Sn(S2COCH2C6H5)2
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2014.1027Keywords:
Organotin(IV), Xanthate, Tolyl/benzyl dithiocarbonate, Crystal structure, AntifungalAbstract
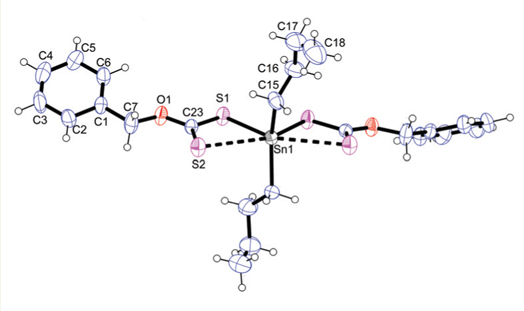
Novel compounds of dimethyl– and dibutyltin(IV) with O–tolyl/benzyldithiocarbonates were successfully obtained by the reaction of Me2SnCl2 and n–Bu2SnCl2 with sodium salt of O–tolyl/benzyldithiocarbonates, [o–, m– and p–CH3C6H4OCS2Na and C6H5CH2OCS2Na], in 1:2 molar ratio in dry toluene. The structure of these newly synthesized complexes has been examined by elemental analysis, FT–IR, multinuclear NMR (1H, 13C and 119Sn) spectroscopy. The thermal behaviour of the complex (8) has been studied by TGA/DTA analysis. The complex (8), n–Bu2Sn(S2COCH2C6H5)2, crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c, in which tin adopts a distorted octahedron or skew trapezoidal bipyramidal geometry accompanied by two n–butyl chains and the two dithiocarbonate ligands coordinated in an anisobidentate fashion. Antifungal activities against fungus Fusarium sp. of these organotin(IV) derivatives exhibited enhanced activity compared to the free ligands.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
License
Except where otherwise noted, articles in this journal are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
